Knowledge Center
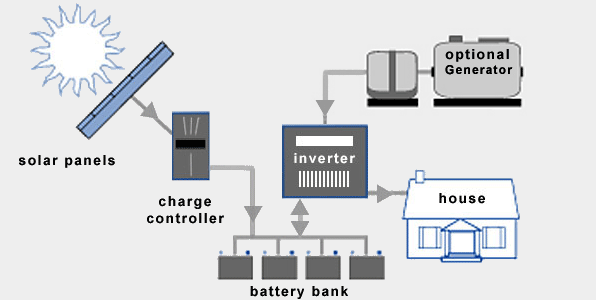
Off Grid Solar Systems
An off-grid system is not connected to the electricity grid and therefore requires battery storage. An off-grid solar system must be designed appropriately so that it will generate enough power throughout the year and have enough battery capacity to meet the home’s requirements, even in the depths of winter when there is less sunlight. The high cost of batteries and inverters means off-grid systems are much more expensive than on-grid systems and so are usually only needed in more remote areas that are far from any electricity grid. However battery costs are reducing rapidly, so there is now a growing market for off-grid solar battery systems even in cities and towns.
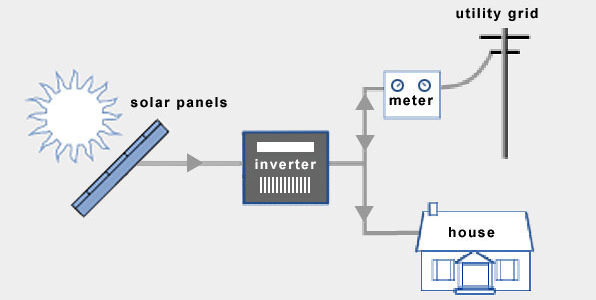
On-Grid System
On-grid or grid-tie solar systems are by far the most common and widely used by homes and businesses. These systems are connected to the public electricity grid and do not require battery storage. Any solar power that you generate from an on-grid system (which is not used directly in your home) is exported onto the electricity grid and you usually get paid a feed-in-tariff (FiT) for the energy that you export.
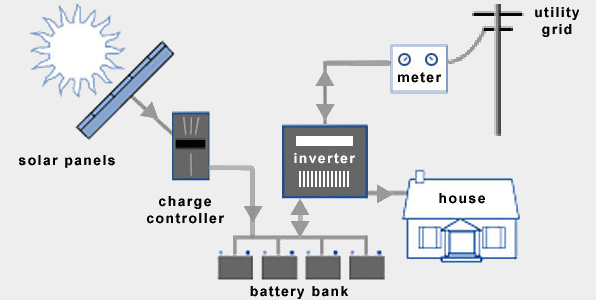
Hybrid System
Due to the decreasing cost of battery storage, systems that are already connected to the electricity grid can start taking advantage of battery storage as well. This means being able to store solar energy that is generated during the day and using it at night. When the stored energy is depleted, the grid is there as a back up, allowing consumers to have the best of both worlds. Hybrid systems are also able to charge the batteries using cheap off-peak electricity (usually after midnight to 6am).